 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783 
Table of contents
When we think of robots, we usually imagine sci-fi-inspired, human-like automatons. While these types of machines are popular now, there are many other kinds of robots operating in the world today.
But let us understand
Let’s begin with some definitions. Most of us are acquainted with the notion of robots but may stumble to depict them as different entities from other machines.
‘Robotic systems are defined as cognitive, interconnected, interactive and physical tools that can sense the environment with the help of sensors, understand events, make plans using algorithms executed in computer programs, and perform actions enabled by actuators’.
Robots are tools that can autonomously sense, plan, act, and respond like humans. They can perform tasks independently, extend human capabilities, and mimic human actions.
Robotics is the area of creating robots. It’s a multidisciplinary specialization where technology, computer science, and engineering assemble to make a human-like machine. Robotics focuses more on the design, construction, operation, and use of robots in various environments.
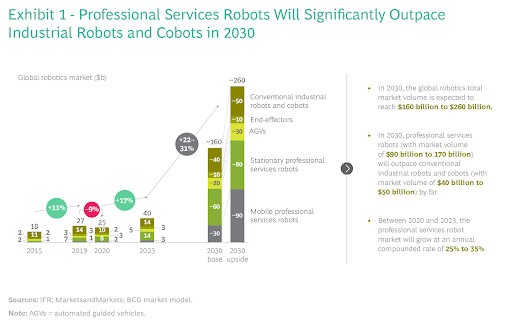
Industrial Robots are anticipated to grow significantly over the coming years. A report estimates that the Robotics sector will be worth $260 billion by 2030. Much of this evolution will come from professional assistance robots that will perform practical tasks for humans, such as cleaning, delivering, transporting, making an appointment, and many more.
The previous few years have introduced remarkable developments and innovations that make our lives more comfortable and beneficial. There is no refuting that the 21st century has brought phenomenal innovations and breakthroughs, from the proliferation and rise of smartphones to the unprecedented development of machine learning, AI, robotics, and autonomous technology. Robotics has gone from fictional movies to real-world scenarios, performing intricate tasks and changing the world we live in.
Robotic adoption is and will likely become a critical determinant of business productivity. Robots can reshape how businesses are accomplished and are intended to bring more automation capabilities to the enterprise. Recent innovations in robotics have delivered several methods to integrate robots into human life.
Robots are already transforming our lives: cleaning robots patrol our living rooms; interactive robots attend to our children; industrial robots help assemble vehicles; medical robots help perform surgeries in hospitals; rescue robots search and save lives in disasters. Top tech firms are in a continued race to transform how robotics are executed in people’s day-to-day lives, leading us to an exciting future.
The line between individual learning and classroom setting is already beginning to blur; cloud-connected home robots are becoming part of our everyday lives. A recent report from Interact Analysis predicts that the annual cobot revenues will reach $1.94 billion in 2028, accounting for 15.7% of the collaborative robot market. These stats show how robots will profoundly affect the future workplace and become capable of taking on multiple organizational roles.
Robots will Create More Jobs.
People have been worried about the power of efficient automation, as they presume that robots will steal their jobs. A report by the PwC estimates that between 2017 and 2037, artificial intelligence and robotics will displace up to 7 million jobs. However, the decrease in expenses caused by AI and robots will generate 7.2 million new jobs, giving a net increase of 200,000 jobs. Robots will always create jobs because change is coming, and some industries will flourish with Robots.
Robotics is an industry that has more than 500 companies making developments that can adequately break down into four types:
Conventional industrial robots and cobots, chatbots.
Stationary professional services (like medical and agricultural applications),
Mobile professional services (like professional cleaning, construction, and underwater activities),
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are used to transport large and small loads in logistics or assembly lines.
One area that is blooming is robotic applications in medicine or healthcare. Robots can impact many healthcare practices, including surgery, rehabilitation, therapy, and mental health. Nevertheless, this industry is heavily dependent on efficiency, precision, and advances in robotics.
The industry is evolving to support this. An International Federation of Robotics report states that the total sales of robotics in healthcare were around $1.9 billion, accounting for 29 percent. A report by Markets and Markets says that the medical robots market is about to reach $16.74 billion by 2023. The most critical applications in Healthcare are in robot-assisted surgery, therapy, and rehabilitation robots- which aid people with a disability or provide physical or cognitive therapy.
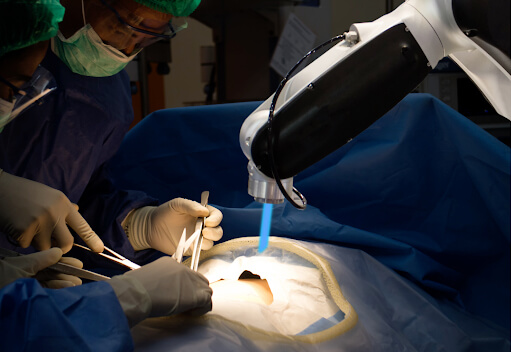
Robotic surgery will have massive potential. Organizations like Microbot, Intuitive Surgical, and Mazor are top industry players in robotic surgery technology. Robot-assisted surgeries are already being utilized in significant procedures by the British National Health Service (NHS). Boston Children’s Hospital in Massachusetts operated alongside doctors to fix a child’s heart valve.
An array of new technologies are transforming the Agriculture Industry. Artificial intelligence, drone technology, 5G, and robotics are helping usher in a new age of farming. Internet of Things technology is becoming more affordable and accessible, speeding up this change. Developments in autonomous technologies assist farmers with driverless tractors, milking robots, automated harvesting systems, and many more.

According to Markets and Markets, the agricultural robot market will increase from $7.4 billion to $20.6 billion by 2025. Different areas within the industry that are likely to experience growth are planting, crop seeding, crop monitoring, fertilization, and irrigation. Robotics will also assist in agricultural areas that lack workers, such as crop harvesting, or hazardous areas, such as pesticide administration. The future of Farming looks promising.
Today, Simulation tools will help us teach robots how to resolve difficulties in the real world. However, this brute force method isn’t adequate because situational complexity often makes it impossible to train robots to respond to unpredictable events flexibly and intelligibly. Nevertheless, new research from OpenAI states that focusing on guiding neural networks to navigate progressively more difficult and randomized environments appears to produce solid results. The first application involves a human-like robotic hand that can solve a Rubik’s Cube without human intervention. This training requires 50 hours of tremendous computing power, using the cloud and distributed computing. Propelled by improvements in computer science, this approach needed to automation will transition from rule-based to goal-based. The robotic capacities that emerge from this shift will be adored in custom production processes.
By 2030, it is estimated that Level 3 autonomous vehicles will account for about 8% of new car sales. Level 3 mobile robots will autonomously navigate efficiently in predefined settings, like a warehouse, signaling or discontinuing when support is needed from a human. At Level 3, the car temporarily drives on relatively unencumbered roads and in clear weather conditions. It cautions the driver to take over when faced with a situation it cannot handle.
Level 4 self-navigation is fully autonomous, with a backup system that can turn the machine off in unexpected situations without human intervention. The capabilities will be perfected around 2030. We can experience self-driving mobile devices in limited environments, like room service robots in hotels or last-mile delivery robots.

The ever-changing geopolitical landscape has motivated more governments to expand their use of robots in warfare. According to Research and Markets, the increase in terrorist activities has been a significant factor in developing robots on the battlefield.
The possibilities of robotics in the military and defense are vast. Robots will not only knock off snipers but also rescue people. We can expect more uses of Robots to help the military with surveillance, intelligence, reconnaissance, search and rescue, combat support, mine clearance, explosive ordnance, and firefighting. Change is coming- 5G technology, more responsive artificial intelligence, and the emergence of smart cities are all likely to accelerate these changes.
A report from McKinsey states that automation and machines will transform our work. The report predicts that activities that require physical and manual skills will drop by 18% by 2030, while those jobs that need primary cognitive skills will decrease by 28%. Ultimately, robots can enhance our lives and shoulder the burden of physically challenging or repetitive jobs. They will help improve Healthcare, make transport more efficient, and give us more freedom to pursue creative endeavors.
Tags: Robotics, Robotics Farming, Robotics Future