 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783 
A database is an organized collection of data that allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and manipulation of information. It provides a structured way to store and manage data, ensuring data integrity and consistency. In the world of digital transformation, databases play a crucial role in various industries, from finance and healthcare to e-commerce and social media, and with their importance, SQL becomes more crucial.
Types of Databases
There are different types of databases, each designed to cater to specific needs and use cases. The two common types are:
Relational Databases: Relational databases organize data into tables with predefined relationships between them. This type of database is widely used and follows the relational model proposed by Dr. Edgar F. “Ted” Codd in the 1970s. Popular relational database management systems (RDBMS) include MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, and PostgreSQL.Non-Relational Databases: Also known as NoSQL databases, non-relational databases store data in key-value pairs, documents, graphs, or wide-column stores. They offer flexibility and scalability, making them suitable for handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. Examples of non-relational databases include MongoDB, Redis, and Cassandra.

Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language for managing and manipulating relational databases. It provides a standardized way to interact with databases, allowing users to create, modify, and retrieve data. SQL is both a data definition language (DDL) and a data manipulation language (DML), enabling users to define database structures and perform operations on the data.
While SQL is a standard language, different database management systems may have their own variations and extensions. For example, SQL Server uses T-SQL (Transact-SQL), while MySQL uses its own SQL flavor. These variations may include additional features and syntax specific to each database system.
In SQL, data types define the kind of data that can be stored in a table column. Some common SQL data types include:
Also Read: 10 Essential SQL Concepts Every Developer Should Know.
Image Source: FreeImages
Relational databases organize data into tables, each consisting of columns (attributes) and rows (records). This design allows for efficient retrieval and manipulation of data. The relational model ensures data integrity and eliminates data redundancy by establishing relationships between tables.
In database design, entities represent real-world objects, while attributes define their characteristics. Relationships describe the associations between entities. For example, in a customer database, the “Customer” entity may have attributes such as “Name,” “Address,” and “Email,” and it may have a relationship with the “Orders” entity.
Functional dependencies define the relationship between sets of attributes in a table. They help ensure data integrity by preventing data duplication or inconsistency anomalies. Database designers can eliminate redundancy and maintain data accuracy by properly identifying functional dependencies.
Keys play a crucial role in database design as they uniquely identify records within a table. The primary key is a unique identifier for a table, while foreign keys establish relationships between tables. Keys help maintain data integrity and enable efficient data retrieval through indexing.
Also Read: How to Design an Efficient Database Schema?
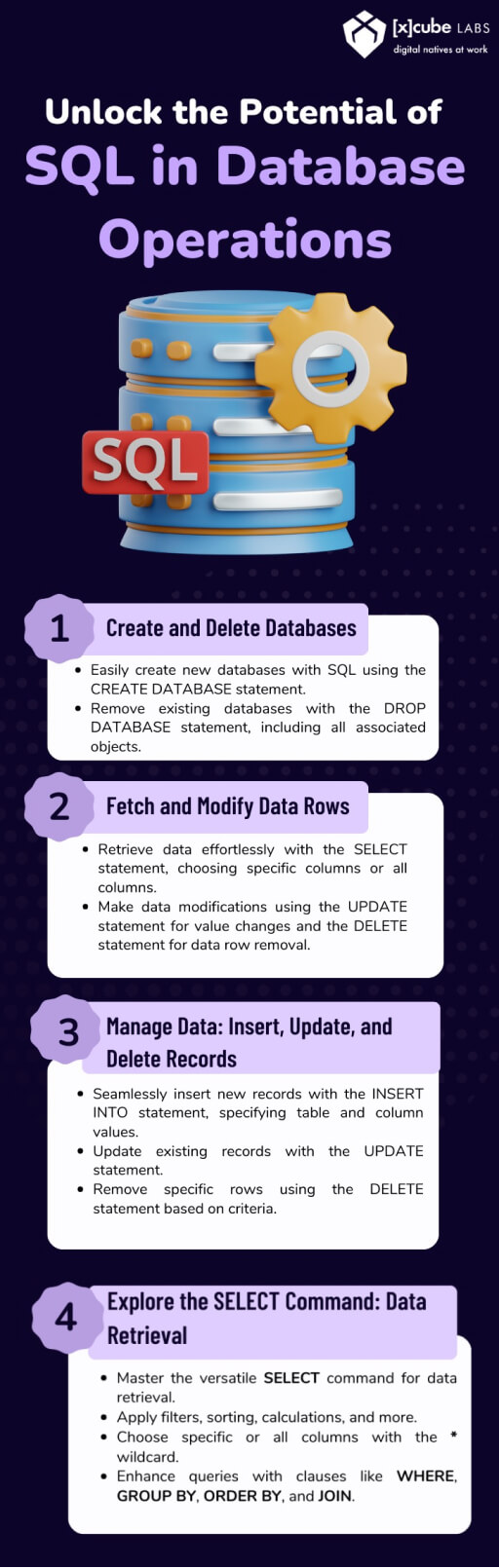
You can create a new database using the CREATE DATABASE statement and specify its name and attributes in SQL. On the other hand, the DROP DATABASE statement is used to delete an existing database, permanently removing all its associated tables, views, and other objects.
SQL provides various commands to retrieve data from a database. The SELECT statement allows you to fetch specific or all columns from one or more tables based on specified conditions. To modify existing data, you can use the UPDATE statement to change values in specific columns and the DELETE statement to remove data rows that meet certain criteria.
You can use the INSERT INTO statement to add new records to a table, specifying the table name and values for the corresponding columns. The INSERT INTO statement allows for inserting data into specific or all columns. As mentioned earlier, the UPDATE statement is used to modify existing records. The DELETE statement, on the other hand, removes specific rows from a table based on specified conditions.
The SELECT command is one of the most commonly used SQL commands. It allows you to retrieve data from one or more tables, apply filters and sorting, perform calculations, and more. Select specific or all columns using the asterisk (*) wildcard. To refine and manipulate the retrieved data, the SELECT command supports various clauses like WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and JOIN.
Indexes are database objects that store a sorted copy of selected columns in a table. They improve query performance by allowing the database engine to quickly locate and retrieve relevant data. By creating indexes on columns frequently used in search conditions or JOIN operations, you can significantly speed up query execution.
SQL query optimization involves analyzing a query’s execution plan and making adjustments to improve performance. Techniques like rewriting queries, optimizing joins, and avoiding unnecessary calculations can enhance query execution time. Proper indexing and statistics collection also contribute to query optimization.
Concurrency control ensures that multiple users can access and modify a database simultaneously without conflicting with each other’s changes. Techniques like locking, optimistic concurrency control, and snapshot isolation help maintain data consistency and integrity in multi-user environments.
Tables are the basic building blocks of a database, representing entities and their attributes. In SQL, you can create tables using the CREATE TABLE statement, specifying the table name, column names, data types, and any constraints. Tables can be altered, renamed, or dropped using appropriate SQL statements.
Views are virtual tables derived from one or more base tables. They allow for customized data presentation, security control, and simplification of complex queries. Views are created using the CREATE VIEW statement and can be updated or deleted as necessary. Views provide a layer of abstraction, enabling users to interact with the data without directly accessing the underlying tables.
Stored procedures, triggers, and functions are database objects that encapsulate specific logic and can be executed as needed. Stored procedures are precompiled sets of SQL statements that perform specific tasks. Triggers are automatically executed when certain events occur, such as data modifications. Functions are routines that return a value based on input parameters.
Also Read: An Overview of Database Normalization and Denormalization.
SQL clauses provide additional functionality to SQL statements. Commonly used clauses include WHERE, GROUP BY, ORDER BY, and HAVING. These clauses allow for filtering, grouping, sorting, and conditional operations on the retrieved data. Understanding and effectively using these clauses can enhance the flexibility and power of SQL queries.
The UNION, INTERSECT, and MINUS operations allow you to combine, compare, and subtract data from multiple tables or queries. The UNION operation combines the result sets of two or more SELECT statements, removing duplicate rows. The INTERSECT operation returns the common rows between two result sets, while the MINUS operation retrieves rows from the first result set that are absent in the second result set.
The GROUP BY clause in SQL allows you to group rows based on one or more columns, and aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, and MAX can perform calculations on grouped data. The ORDER BY clause sorts the result set based on specified columns and sorting conditions.
Joins allow you to combine data from multiple tables based on related columns. Inner joins retrieve records with matching values in both tables, while outer joins retrieve matching records as well as unmatched records from one or both tables. Self joins are used when a table is joined with itself, and cross joins produce a Cartesian product of all rows from two or more tables.

Data constraints ensure the integrity and consistency of data in a database. Common constraints include primary key constraints, unique constraints, foreign key constraints, and check constraints. These constraints enforce rules on the data, preventing invalid or inconsistent values from being inserted or updated.
Database systems have built-in mechanisms for managing user access and permissions. Database administrators can grant permissions to users or roles, specifying the level of access they have to objects such as tables, views, stored procedures, and functions. Properly managing permissions is crucial for maintaining data security and confidentiality.
Sequences are database objects that generate unique numeric values. They are commonly used to generate primary key values for tables. In SQL, you can create sequences using the CREATE SEQUENCE statement and reference them when inserting records into tables. Sequences provide an automatic and efficient way to generate unique identifiers.
Transactions ensure the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID) properties in database operations. A transaction represents a set of database operations that should be treated as a single unit. SQL provides commands like COMMIT, ROLLBACK, and SAVEPOINT to control transaction behavior. COMMIT saves the changes made within a transaction, ROLLBACK undoes the changes, and SAVEPOINT marks a specific point within a transaction to which you can roll back if needed.

To retrieve a list of users and their permissions in SQL Server, you can query system views like sys.database_permissions, sys.database_principals, and sys.server_role_members. These views provide information about database-level and server-level permissions assigned to users and roles.
SQL is a language used to operate databases, while MySQL is a specific relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses SQL as its language. SQL is a standard language that can be used with various RDBMS, including MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and PostgreSQL.
In SQL, the INT data type is used to store integer values, such as 1, 2, -5, or 1000. The DATE data type is used to store dates, such as ‘2023-10-30’. The BIT data type is used to store boolean values, represented as 0 or 1.
To restore an SQL database from MDF and LDF files, you can use the RESTORE DATABASE statement, specifying the backup file and the destination database name. The MDF file contains the primary data file, while the LDF file contains the transaction log. By restoring these files, you can recover the database to a specific point in time.
In conclusion, SQL is a powerful language for managing and manipulating relational databases. It allows users to create, modify, and retrieve data, ensuring data integrity and efficient data operations. Understanding SQL and database concepts is essential for anyone working with databases or looking to pursue a career in database administration or development. By mastering SQL, you can effectively design and interact with databases, optimize query performance, and ensure data security and integrity.