 1-800-805-5783
1-800-805-5783 
“The emergence, adoption, and hype around digital twins are growing. Digital leaders should drive discussions with their business unit peers on the potential business value of digital twins, and their limitations in IoT and digital businesses, while driving policy on their architecture and use.”
-Gartner
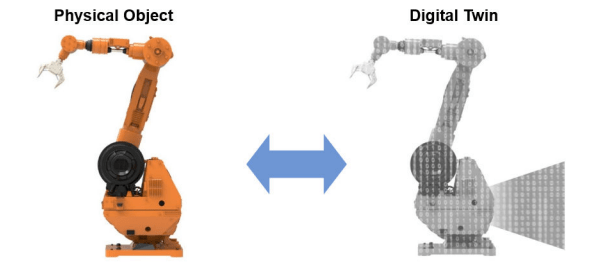
A term coined by NASA, “digital twins” refers to a virtual model of a physical product, process, or a service. NASA introduced digital twin to solve huge complicated challenges they were facing in their early days of space exploration.
The major challenge was how can they operate, monitor or repair systems which were impossible and beyond their engineer’s ability to physically monitor or modify. Pairing technology helped NASA during the hapless Apollo 13 occurrence. The innovation of mirrored systems rescued engineers and astronauts from the problem that occurred in the space from the earth.
NASA’s innovation “digital twin” utilizes data from sensors that are installed on real objects. Now, this technology is being used to develop a new direction, roadmaps, and next-generation aircraft and vehicles.
John Vickers, NASA’s leading manufacturing expert and manager of NASA’s National Center for Advanced Manufacturing, said, “the ultimate vision for the digital twin is to create, test and build our equipment in a virtual environment. Only when we get it to where it performs to our requirements do we physically manufacture it. We then want that physical build to tie back to its digital twin through sensors so that the digital twin contains all the information that we could have by inspecting the physical build.”
The idea of a digital twin has already existed for the past decades. With the evolving technologies, it has successfully pinned fifth on Gartner’s Top 10 strategic technology list for 2017.
Digital twin is a technology that pairs physical objects and virtual model to monitor systems and analyze data. It uses sensor data to find and fix the problems in advance, predict and plan for the future. And that brings in a new opportunity for enterprises to stay ahead in this digital world by utilizing simulations. According to Gartner, there are four core elements of digital twins:
“By 2020, there will be more than 21 billion connected sensors and endpoints, and digital twins will exist for potentially billions of things.”
-Gartner
PwC report says, according to Colin J. Parris, Vice President of Software Research at the GE Global Research Center, digital twin uses sensors to gather the data first. He describes digital twin models perform in three stages:
Source: Gartner
Digital Twins are raised amongst a history of innovations and insights. Digital modeling such as computer-aided design (CAD) is designed for enterprises to pull key benefits from complex assets. The technology allows enterprises to trace their products throughout their development period. The technology helps them in the decision-making process that is affiliated with physical products.
Gartner predicted, “billions of things are going to have digital twins in the next five years because the number of devices will be able to interface data keeping Internet of Things as the base.
Enterprises foresee the significant value that digital twin technology can add to their business operations by optimizing assets and minimizing defects. Gartner described a digital twin is that it provides physical objects digitally within the appropriate software tools, so it can instantly monitor and perhaps even control them.
Digital twins have taken the modeling to a whole new level. It renders a real opportunity to the enterprises to understand customer’s needs and boost customer experience.
Imagine the fusion of a smart upshot specialist paired with advance device tracking abilities that bring out the advance business models to drive revenue and help enterprises in various aspects to enhance their business. For example, the designer can inspect and monitor which part of the design needs replacement keeping the safety matter on the priority list that may occur in the future, without being in physical proximity to them.
The idea behind creating digital twin technology is to make everyday decisions about the physical world. However, we see few industries started using this technology and among them, one of the adopters is manufacturing industries. But, International Data Corporation (IDC) predicted that by 2018, enterprises investment on digital twin technology will see 30% rise in cycle times of their critical processes.
Manufacturing industries such as vehicle manufacturers can mock-up the model into 3D visualizations. This will help them to monitor which parts need attention if it requires any replacement. Once they find it, fix it or notifying their relevant team to repair and review the quality of the vehicles. Digital twins can be used to plan preventative maintenance that will help manufacturers to eliminate problems before it arises. Other benefits from digital twin technology are that they enable operators to minimize their company’s production costs, downtime and evolve insights to perform better and faster at low cost.
Gartner has envisioned new business models emerge, facilitated by digital twins. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are the means of injecting intelligence into new and existing apps to form the smart digital network. They are shortly progressing to be embedded into everyday equipment such as appliances, speakers, and hospital equipment. This phenomenon aligns with the emergence of conversational systems, the expansion of the IoT into a digital network and the trend towards digital twins.
Well, this is just the tip of the iceberg, there’s still a lot more to explore and test its potential. When digital twins – the digital portrait of physical systems is integrated properly it allows you to have a better understanding of ongoing operations. Also, it helps you to predict the future to improve your business performance.
Tags: Digital Technology, Digital Twins